Formaldehyde manufacturing technologies
It is a vital chemical used in various industries, including plastics, textiles, and pharmaceuticals. Its production involves several processes, each with its unique characteristics and challenges.
Production Process Options
There are several ways to produce CH2O, including reducing carbon oxides, oxidizing hydrocarbon gases, and oxidizing methanol.
Reduction of Carbon Oxides
The reduction of carbon oxides involves the reaction of CO with H2 to form HCHO:
- CO + H2 → CH2O
This is simple and relatively inexpensive but has limitations due to the availability of raw materials.
Oxidation of Hydrocarbon Gases
The oxidation of hydrocarbon gases involves the controlled reaction of hydrocarbon gases with air or oxygen. For example, the oxidation of methane can be represented by the following reactions:
- CH4 + ½O2 → CH3OH
- CH3OH + ½O2 → CH2O + H2O
- CH2O + O2 → CO + H2O
- CH2O + O2 → CO2 + H2O
The yield is often low, and the reaction can produce unwanted byproducts.
Oxidation of Methanol
The oxidation of CH3OH is a widely used method for formol production. This synthesis involves the reaction of carbinol with air or oxygen over a catalytic material. The reaction can be represented by the following equation:
- CH3OH + ½O2 → CH2O + H2O
The oxidation of methyl hydrate can be carried out using different reaction agents, including Luna, iron-molybdenum oxide, and vanadium oxide.
Methanol Processes
The monohydroxymethane routine is the most common method of formol production. This mechanism can be classified into two main groups: oxidative-dehydrogenation and pure oxidation.
Oxidative-Dehydrogenation Process
The oxidative-dehydrogenation production uses a metallic enhancers, such as silver, to oxidize Methylic alcohol to Methyladehyde. The reaction is reversible, and the yield of Methanal depends on the reaction conditions. The reaction can be represented by the following equations:
- CH3OH → CH2O + H2
- H2 + ½O2 → H2O
The method is typically carried out at temperatures between 600-700°C and pressures of 1-2 atm.
Pure Oxidation Technique:
Various Catalytic Metals Considered for Formic aldehyde Production
The choice of activation substance is crucial in formalin production. Some common activating materials used in the pure oxidation approach include iron oxide-molybdenum oxide, vanadium oxide, and tin vanadate.
Operation Conditions
The operation conditions for formaldehyde solution production vary depending on the system and reaction enhancers used. Typical operation conditions include:
- Temperature: 200-700°C- Pressure: 1-5 atm- Catalyst: silver, iron-molybdenum oxide, vanadium oxide, or tin vanadate- Feedstock: methylalchol, hydrocarbon gases, or carbon oxides
The Silver Catalyst Synthesis for Formalin Production
The silver derivative agent mechanism is a widely used method. This treatment involves the oxidation reaction of carbinol to formaldehyde, which is catalyzed by Ag. The reaction is as follows:
CH3OH + ½O2 → HCHO + H2OΔH = -156 kJ/mol
Manufacturing Description
The transformation begins with the vaporization of pyroxylic spirit in a heat exchanger. The spirit vapors are then mixed with air and passed through a reactor containing a bed of pure Ag in a granular crystalline form. The reactor is supported above a steam boiler, allowing the reaction products to pass through the boiler tubes and produce steam.
Reaction Mechanism
The Ag-catalyzed setup produces CH2O through the oxidation and dehydrogenation of monohydroxymethane. The reaction mechanism involves the following steps:
1. CH4O vaporization2. Mixing of its vapors with air3. Reaction of CH4O with oxygen on the Argentum catalyst4. Formation of HCHO and water
Process Conditions
- Temperature: 149.6°C (reactor inlet) to 343°C (reactor outlet)- Pressure: 28 psi (reactor inlet) to 25 psi (reactor outlet)- Feed stock conversion: 87.4%- Yield: 99% (in the formalin absorber)
Equipment Description
The equipment used in the flow diagram primarily are:
- Heat exchanger for alcohol vaporization- Reactor with a bed of pure Argentum in a granular crystalline form- Steam boiler for producing steam- Formalin absorber for separating methanal and water- Distillation column for separating methanol and methanal
Rate Expression
The rate expression for the silver-catalyzed reaction is as follows:
- -rm [mole/g catalyst hr] = k1 pm / (1 + k2 pm)
where:
- rm is the reaction rate- k1 and k2 are constants- pm is the partial pressure of methanol
The constants k1 and k2 are defined as follows:
log10 k1 = 11.43 - 3810/Tlog10 k2 = 10.79 - 7040/T
where T is the temperature in Kelvin.
Formalin Absorber
The formalin absorber is a critical piece of equipment in the Luna catalyst pure oxidation method. It is designed to separate methyladehyde and water from the reaction products. The absorber has 10 trays, each with an efficiency of 30%. If simulation issues arise, a component separator can be used in place of the absorber.
Material balance over the types of equipment:
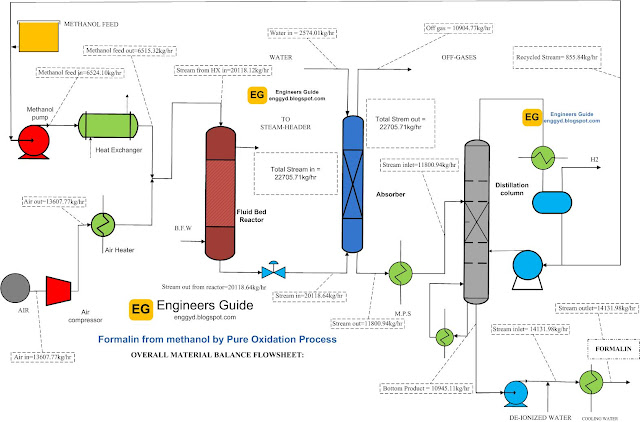 |
| Flow diagram with the material balance over the equipment of Formalin chemical |
Formic aldehyde production involves several routines, each with its unique characteristics and challenges. The choice of facilitator and reaction conditions is crucial in determining the yield and selectivity of formalin. Manufacturers can optimize their operations and produce high-quality methylene glycol for various industrial applications by understanding the different production options and catalytic materials substances.
